Can Chocolate companies use Blockchain to Eradicate Slavery In The Chocolate Industry?
Everyone loves chocolates but not all are aware of the dark depths of the industry.

The dank underbelly of cocoa production is filled with horror stories of child labor and even slave labor, especially in major cocoa-producing countries, such as Cote d’Ivoire and Ghana. Major chocolate brands, such as Nestle and Hershey are aware of this problem and have even acknowledged the use of child labor in the cocoa fields. Despite this, most major chocolate companies fail to act against it and stop child enslavement.
According to a report by Ex pert Market Research, the global cocoa market was priced at an astonishing USD 11 billion at the end of 2020. The report predicts the global cocoa industry to grow to as much as USD 13.5 billion by 2026, at 3.4% CAGR. A study by the International Cocoa Organization forecasts global cocoa production to reach as much as 5.02 million tons by end of 2021. These statistics depict the enormous size of the cocoa industry worldwide.
To make the industry safer and more sustainable, several chocolate companies have integrated blockchain technology into the cocoa supply chain with surprising effectiveness.
Major Challenges Faced by Chocolate Companies Stopping them to be 100 Percent Slave-Free
The cocoa has to go through several stages in the supply chain to reach from the farmer to the consumer. Most cocoa farmers sell their produce to a pisteur, who buys the cocoa from farmers and transports them up to the port for export. In the meanwhile, the pisteur can also sell the cocoa to third-party vendors before it reaches the port. Here, the cocoa is then sold to exporters who sell it to cocoa traders, who in turn, essentially control the entire cocoa market.
A very complicated supply chain with multiple vendors ensures that the farmer is unable to get a fair price for cocoa beans. As a result, most farmers turn to child labor or modern-day slavery to make cocoa production more feasible.
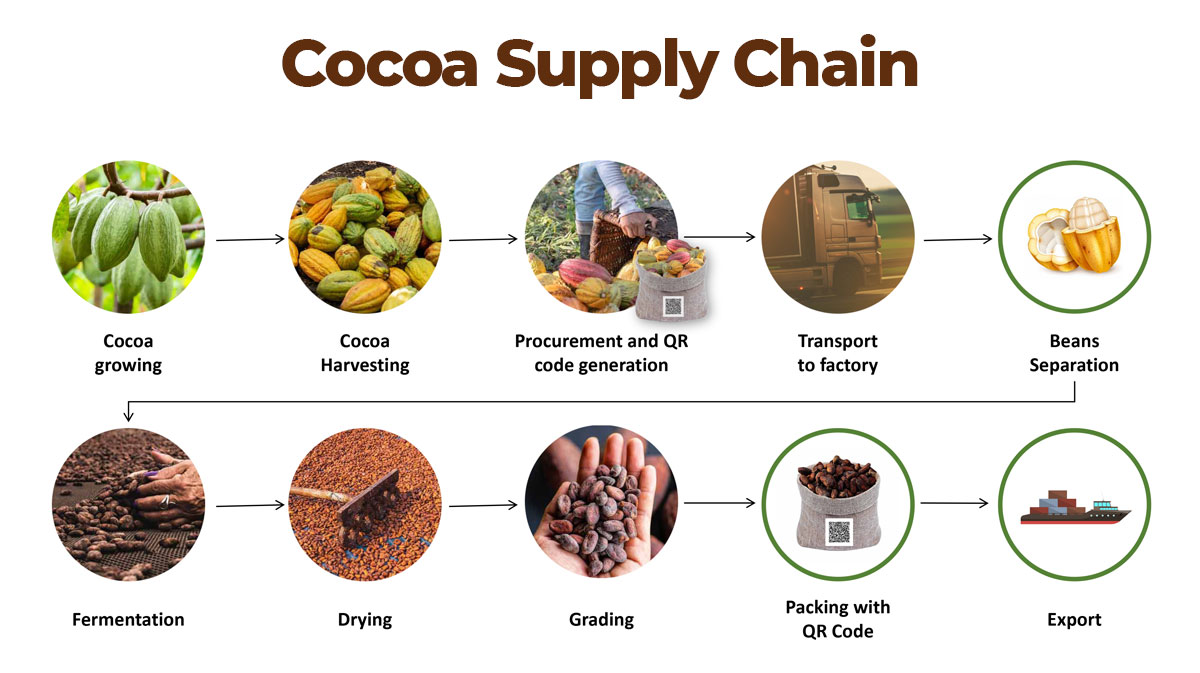
Farmers have no control over this complicated supply chain or the price of cocoa. Eventually, this keeps the farmer in poverty which often turns them to cheaper labor in the form of child labors. Studies show that around 30,000 children are trafficked annually to serve as child labors in cocoa fields. Besides, the farmers are unable to purchase modern machinery for growing cocoa which makes them increasingly dependent on the cheap but unethical child labor force.
Obstacles for Blockchain use for Traceability in the Cocoa Industry?
Lack of traceability and control are the main obstacles for blockchain use in the cocoa industry. However, the technology is proving immensely successful in making the cocoa industry safer and more sustainable.
Let’s check some practical advantages of using blockchain technology in the cocoa supply chain:
1. Integrates transparency and Traceability
A major benefit of integrating blockchain technology into the cocoa supply chain is that it eases communication and validates cocoa products as being produced using safe and ethical methods. Every participant in the blockchain supply network is provided with a copy of the public ledger which contains comprehensive information of the product flow within the supply chain. Any alterations in the existing data are accessible to all participants. This makes the supply chain completely transparent for users and they are able to track products from origin. This way, blockchain can shift the trust-based supply chain to a more feasible automated mode. Thus, blockchain technology is extremely useful for making the cocoa supply chain incredibly transparent and traceable.
However, the lack of advanced technology at the farmers’ end is proving to be a major obstacle in implementing blockchain technology in the cocoa industry. Food majors have begun accelerator programs to enroll their farmers to be trained via smartphones to manage their farm, crop and finances.
2. Makes farmers stronger
Implementing blockchain technology will help strengthen the farmers. This technology allows farmers to have direct access throughout the global cocoa market by helping to avoid the need for intermediaries and middlemen from the cocoa supply chain. This way, the farmer is able to receive updated cocoa prices directly from the market as and when it fluctuates. This results in the farmers getting the bargaining advantage in the market and making higher profits in turn.
As a result, the farmer will be able to hire skilled labor for a higher price and even employ modern farming methods and machinery to make cocoa production more sustainable and safer.
3. Helps with effective marketing
Apart from integrating transparency, traceability and sustainability into the cocoa supply chain, the use of blockchain technology also proves excellent for marketing. This technology has the potential to allow companies to achieve the desired level of trust and repute in the market through its credible blockchain-based operations.
Conclusion
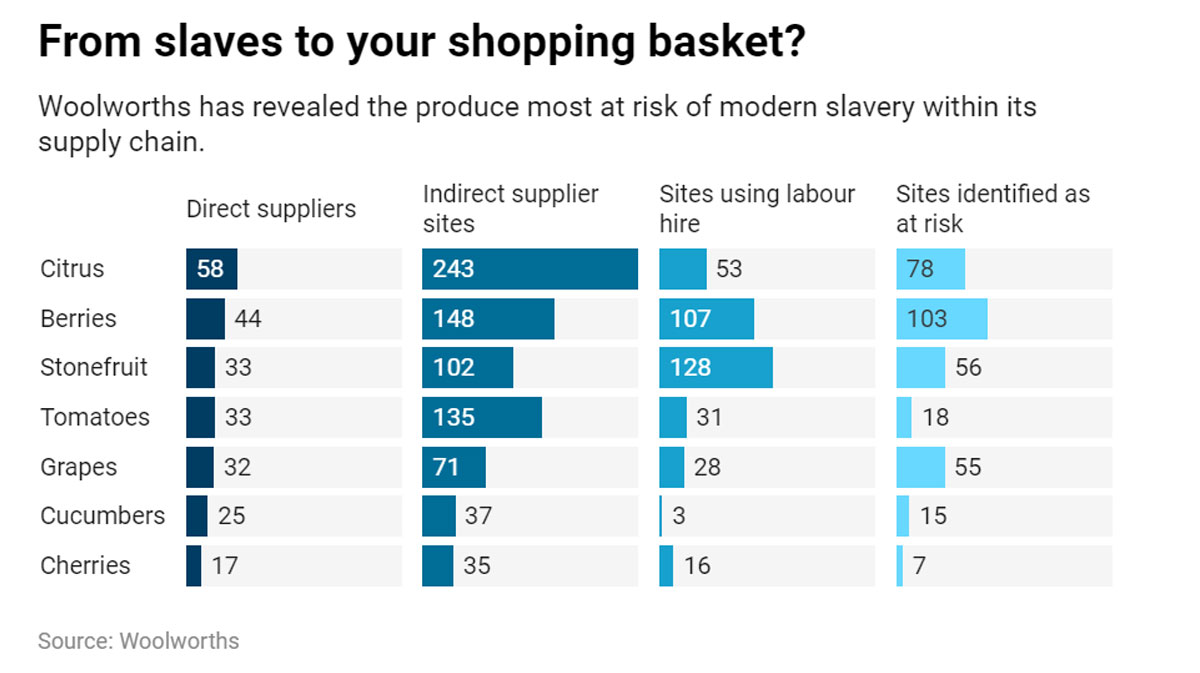
According to a recent report by Woolworths modern slavery, citrus farms and Australian berry have the most risk of having slave-like working condition.
This situation is despite the Modern Slavery Act that was introduced in the year 2018. The Act requires companies to periodically review their supply chains and check if the factory workers are exploited, face human trafficking, forced labour or are working in other poor conditions.
Few highlights prevalent in the agri-food sector:
● The first statements have been released by the Big supermarkets under new modern slavery laws.
● The reports also reveal that the companies are unaware of working conditions at the farms that supply them with fruit.
● In 2018, over half of 638 harvesting businesses investigated by a Fair Work Ombudsman found a breach in workplace laws.
Using blockchain technology to capture the right data sets in the agricultural production sector seems to be a step towards optimizing not just the cocoa supply chain, but fresh fruits and vegetables, aquaculture. This technique also has the potential for incredible industrial growth as the data is tamper-proof and large food brands must ramp up their supply chains and food handling to enable the accuracy of details like who the farmer is, their background, wages, working conditions etc.
SourceTrace’s DATAGREEN has been used by some of the large organizations for the purpose of social audit within their complex value chains. Reach out to us and we can help you address this dark problem with data and analytics.
SourceTrace's software solutions have been deployed across 37 countries and 4 continents already. We are on a mission to make agriculture and food systems more sustainable. Get in touch and we will extend our expertise and commitment to you.
Request a Demo


